Exploring the Differences Between THC and HHC: A Guide for Hemp Enthusiasts
As the hemp and cannabis industries continue to evolve, more cannabinoids are being discovered and explored for their unique properties and benefits. Two such cannabinoids that have garnered attention are THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and HHC (hexahydrocannabinol). While they share some similarities, THC and HHC have distinct characteristics that set them apart. In this article, we’ll delve into what THC and HHC are, their differences, and the unique benefits they offer.
What is THC?
THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the most well-known cannabinoid, primarily responsible for the psychoactive effects associated with cannabis. It interacts with the endocannabinoid system in the brain, particularly the CB1 receptors, to produce its characteristic “high.”
Key Characteristics of THC:
- Psychoactive: THC is known for its psychoactive effects, which can include euphoria, relaxation, altered sensory perception, and increased appetite.
- Medical Benefits: Beyond its recreational use, THC has been studied for various medical applications, including pain relief, reduction of muscle spasticity, appetite stimulation, and anti-nausea effects.
- Legality: The legal status of THC varies widely. While it is legal for medical and recreational use in some states and countries, it remains illegal in others. In the United States, hemp-derived THC is federally legal if it contains less than 0.3% Delta-9 THC.
What is HHC?
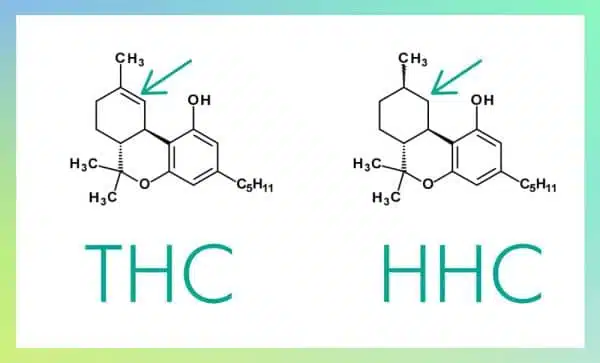
HHC, or hexahydrocannabinol, is a hydrogenated derivative of THC. While it naturally occurs in trace amounts in the cannabis plant, it is typically produced synthetically from hemp-derived CBD. HHC is relatively new to the market, and research into its effects and benefits is still emerging.
Key Characteristics of HHC:
- Mildly Psychoactive: HHC is reported to have psychoactive effects, but they are generally milder compared to Delta-9 THC. Users often describe the high as more relaxed and less intense.
- Chemical Structure: HHC is created by adding hydrogen atoms to THC, altering its chemical structure and stability. This hydrogenation process makes HHC more resistant to oxidation and degradation, potentially giving it a longer shelf life.
- Potential Benefits: Early anecdotal reports and preliminary research suggest that HHC may offer benefits similar to THC, such as pain relief, relaxation, and appetite stimulation, but more research is needed to confirm these effects.
The Differences Between THC and HHC
While THC and HHC share some similarities, their differences create distinct experiences and potential applications.
Key Differences:
- Psychoactive Effects: THC is known for its potent psychoactive effects, while HHC provides a milder high. This makes HHC a potential option for those who want to experience the benefits of THC without the intense psychoactive effects.
- Chemical Stability: HHC’s hydrogenated structure makes it more stable than THC, meaning it is less likely to degrade over time. This can result in a longer shelf life for HHC products.
- Legality: HHC exists in a legal gray area. Since it is derived from hemp and not explicitly listed as a controlled substance, it may be legally available in areas where THC is restricted. However, it’s crucial to check local regulations as laws regarding cannabinoids are continually evolving.
- Availability: THC is widely available in regions where it is legal, both for medical and recreational use. HHC, being newer and less well-known, may be harder to find and is typically available through specialized retailers.
Consumption Methods
Both THC and HHC can be consumed in various forms, offering flexibility based on individual preferences and needs.
Popular Methods:
- Vaping and Smoking: Both THC and HHC can be vaped or smoked, providing quick onset of effects, making them ideal for immediate relief from symptoms like pain or anxiety.
- Edibles: Offer a longer-lasting and more gradual onset of effects, suitable for sustained symptom relief and overall relaxation.
- Tinctures and Oils: Allow for precise dosing and can be used sublingually (under the tongue) for faster absorption or added to foods and beverages.
- Topicals: Can be applied directly to the skin for localized relief of pain and inflammation without psychoactive effects.
Legal Considerations
The legality of THC and HHC varies widely by region. THC is strictly regulated and may be legal for medical or recreational use depending on local laws. HHC, on the other hand, is often found in a legal gray area due to its status as a hemp-derived cannabinoid. It’s essential to stay informed about your local regulations regarding these compounds to ensure compliance.
Conclusion
THC and HHC each offer unique benefits and experiences for hemp enthusiasts. Whether you’re seeking the potent psychoactive effects of THC or the milder, more stable experience of HHC, both cannabinoids provide valuable options for various needs. As always, it’s important to start with a low dose and consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications. Explore the potential of THC and HHC and discover how these cannabinoids can enhance your wellness journey.
